The Internet offers endless ways to reach customers around the world, beyond those who can visit stores in person. In fact, some companies operate without a single physical store.
This digital shift has been decades in the making, and more than ever, businesses that sell goods need to invest in e-commerce. Organizations that haven’t moved their sales transactions online can still make the leap to virtual storefronts, but business requires planning to ensure they can create a successful online presence and ensure continued success.
In addition to the resources, planning and tools required for successful virtual storefronts, businesses must prioritize online customer interactions. Organizations need to consider several key areas when beginning an e-commerce planning process.
1. Define general goals for e-commerce
While an organization may have the ambition to increase its global sales, e-commerce affects the way it does business. Leadership teams must establish their primary business goals when adopting e-commerce and determine how the new strategy will align with the company’s vision and goals. E-commerce is an extension of the organization, so if it doesn’t align with business goals, the business likely won’t grow or gain a wider audience.
2. Allocate resources to support electronic commerce
Online sales don’t always require a person to receive and process payments, so e-commerce uses resources, such as automation, to process orders and resolve customer questions or issues. For example, FAQ pages and chatbots can answer simple customer questions about order status or shipping information.
These dedicated resources can ensure that customers have positive experiences, which can influence their return.
3. Align marketing and sales strategies
The Internet offers an opportunity for organizations new to e-commerce to reach customers thousands of miles away. However, this reach also means that sales and marketing teams must change their strategies and embrace social media and search engine optimization to reach both potential and existing customers online.
E-commerce sales and marketing strategies can also introduce online advertisements and the ability to resell products on various online marketplaces, such as Amazon and eBay.
4. Define target customers and their needs
Organizations should establish their ideal online clientele. After defining their target audience, sales and marketing teams can update their efforts and campaigns to reach these people and support their online shopping experiences.
Understanding your target audience can also influence how design teams create the organization’s online catalog, as some products may require customers to customize the product or service they want.
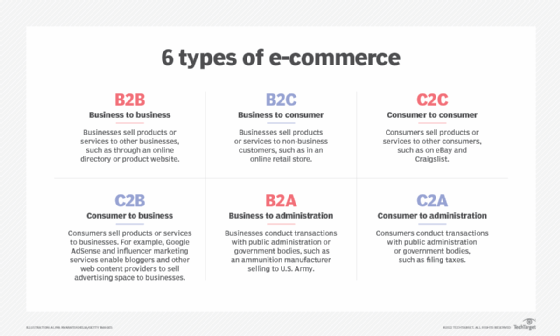
Amidst the e-commerce planning process, organizations should know what type of e-commerce their business falls into.
5. Create a customer service plan
An organization’s overall business strategy requires customer service, and e-commerce is no different. Organizations should establish processes and procedures to respond to customer inquiries, cancellations or general questions received electronically or by phone during the purchase process.
Larger organizations may require a call or contact center to support online sales, as the volume of purchases may be high enough to require 24/7 global customer support.
6. Invest in the right technology
E-commerce software vendors have simplified implementation over the years. Many vendors, such as Shopify, offer online stores that organizations can plug and play into their existing websites.
Before businesses choose e-commerce software, they should define their e-commerce requirements, the type of catalog and the overall product options they need.
7. Identify the integration requirements
After an organization invests in an e-commerce platform, it must address integration with its existing internal systems and vendors. This process may include integrating the online store with an internal inventory system to display stock levels, a system to generate shipping labels, accounting to post all sales to a financial platform, or integrating the conversion rate for pricing products in foreign currencies.
8. Create KPIs for online sales
Sales teams should manage and monitor online sales just like traditional storefront sales. After these teams add e-commerce to their regular funnels and forecast reviews, they need to continually evaluate online sales performance to ensure they’re succeeding.
Online sales teams also need to have goals they can evaluate to assess trends and potential changes that could be made if online shopping declines.
9. Seek continuous improvement
Leadership teams must keep up with changes in their own marketincluding new competitors, marketing channels, customer desires, and ways to improve internal operations to get products to customers quickly and efficiently.
E-commerce teams can build an online store quickly, but up-front planning can help ensure the site attracts enough sales to drive revenue. Planning also helps companies allocate resources efficiently, understand their goals and put KPIs in place to verify that their e-commerce strategy is successful.
[ad_2]
Source link




