AI search is undoubtedly the hottest topic in digital marketing right now. I worry that SEO newbies might think that all they need is an AI chatbot to “get rich quick”. When everyone and their aunt is pushing the next big thing, I try to be cautious and resist the initial hype.
At the end of the day, focusing on the fundamentals: optimizing your website, creating content and attracting links still drives SEO results today.
But if you want to up your game and get ahead of the competition, I’m going to share SEO opportunities worth investing in this year.
SEO Opportunities to Seize in 2023
Instead of joining the AI bandwagon, I decided to take the “road less traveled” and look to Google’s own resources.
What did Google highlight more and more in late 2022 and early 2023? What shows up prominently in Google results and drives an increase in analytics without too many people pushing it?
Below are the things I noticed.
1. Google’s new focus: useful content
The fallout from the release of the Useful Content Update (HCU) was underwhelming. But soon after, Google declared it a permanent search ranking system, not a one-time event. Since then there have been more related updates that had prominent effects on websites.
HCU initially did not significantly affect automated websites.
Emphasizing useful content rather than simply “quality content” is a paradigm shift. Google has focused on quality for years, so this is a massive shift in their philosophy.
Google’s guidance has always been along the lines of “create great content and the rest will follow.” Over time, they have become less dependent on links and can now determine the quality and usefulness of content algorithmically.
If you’ve followed Google’s advice, chances are your site is full of high-quality content. Good for you! But nowadays, that’s not enough.
We’re used to seeing quality content that gives context, cites sources, or provides additional links. Useful content is more than that.
To be truly useful, your content must exhibit the following characteristics:
Show experience
Helpful content is written by subject matter experts who know how things work from first-hand experience.
Instead, fully automated AI content or other cheap, mass-produced content just abstracts from other sources found on the web. It is second-hand and not based on experience, equivalent to hearsay or gossip.
Solve specific problems
Quality content is more journalistic. You should check sources, verify information, and follow other links for additional context and information.
Useful content, on the other hand, solves particular problems early on and:
It doesn’t distract but offers what people need when they need it. Not happy for the sake of content. It’s not made for virality. It has a specific use case. Explain how to fix a common problem or treat a known problem. It provides a standalone solution that doesn’t require a click to go back to Google. Provides additional links and resources if the user wants to read more about the same topic.
Offers helpful tips
Helpful content explains a solution in general terms i provides step-by-step actionable tips for implementation.
For example, many “how to start a blog” guides only explain how to set up WordPress, although it is usually prepared with many hosting providers and to buy hosting (from the company that pays the highest affiliate fees).
However, these “blogging guides” say nothing about how to write for a blog, how to get ideas (beyond keyword research), or how to get people to come to you (it’s not just about outreach ).
Also, these guides, aimed at generating as much affiliate income as possible, will never tell you how hard it is to maintain a blog and update it regularly, let alone gain traction.
Helpful tips are needed here, not what the site owner wants (make more money), but what the visitor wants to do (learn how to blog).
It helps by itself
Useful content does no require you to fill out a form, register, make a payment, or click back through Google search results to be helpful. Ideally, the page should have all the information the user needs, not a traffic site or “blog spam” that links to other sites.
Helpful content is not intended to distract, attract attention, and sell a product or service. To update your content and make it useful, you can:
Answer specific questions. Make the body text readable/scannable. Provide and/or list solutions. Optimize for specific user intent.
Recognize your existing content as an opportunity. Invest resources to turn them into useful parts by solving problems that people ask for (see the last section).
Get the daily search newsletter marketers trust.
2. Google People-Based Ranking Criteria: EEAT
EEAT is another notable change in Google’s guide to search quality. Experience is a significant addition to the popular concept of expertise, authority and trustworthiness.
At first, I thought Google meant user experience, but I was wrong.
While they like clean UX, especially web pages cluttered with above-the-fold ads and optimized for site speed, UX is not part of EEAT.
The new “E” in EEAT refers to the actual experience of the people who created the content. Google aims to reward first-hand experience. Again, it’s clear they want to rank content from people familiar with a topic rather than just auto-generated content.
AI tools do not have first-hand experience in handling many manual processes. Simply put, AI can’t cook, do yoga, or play basketball. He can only study existing theory and content and paraphrase it.
Although AI can drive a car, direct missiles and chat, it’s usually not the same AI that generates the content. Unless yours Tesla AI bot start blogging about commuting, there is no first-hand experience to benefit from.
Gain a competitive edge by finding the right people and getting them to write for you. We are talking about experienced subject matter experts which also exhibit authority on the web and have gained considerably to trust of the hearings.
Either you invest in yourself, your team and the necessary skills in your particular area or you approach people who already have them.
This is an excellent opportunity to stand out and differentiate yourself from the sea of mediocre mass-produced and often automated content.
In an age of over-the-top AI content, Google wants to empower people who care and are knee-deep in their subject matter. EEAT is an obvious proof of this.
3. Google’s favorite SERP feature: “People also ask” questions
To ensure you’re delivering useful content, respond to real demand. There’s no better way to do this than to look at Questions People Also Ask (PAA). Google already shows them below most of the top search query results.
I realized that PAA questions are beneficial for my SEO when I started getting thousands of visitors for one of the most popular browsing queries on the web. No, it wasn’t [google] or [facebook] but close: [twitter].
I was skeptical because I’ve experienced worthless crashes and traffic spikes. Not this time. After further research, I became a fan of PAAs.
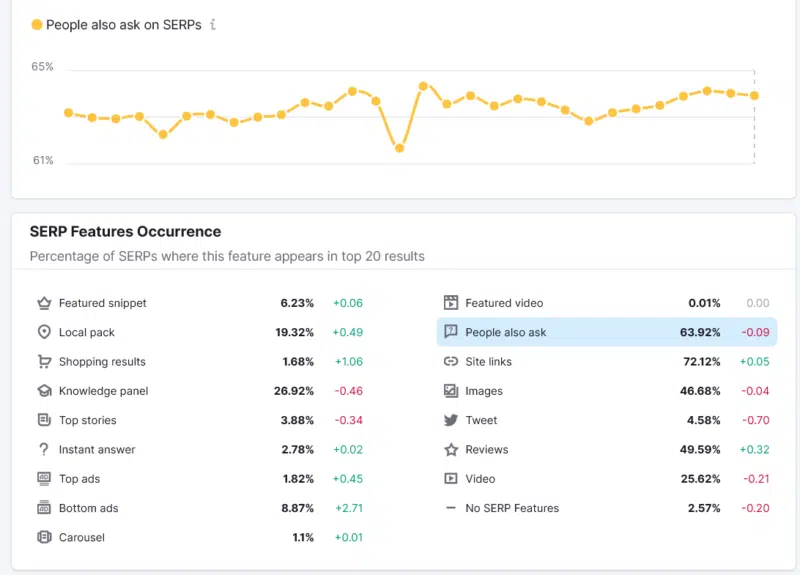
PAAs are not new. They have been widespread for several years and exploded in 2019. The PAA feature appeared half as often in July 2022, but has recovered since then.
As of January, 64% to 70% of search results had PAA RankRanger i Semrush data This makes PAA the second most important SERP feature after sitelinks.
Enjoy their traffic benefits while they’re nearby. In the past, we had to exploit third-party resources such as:
Forums (Facebook and LinkedIn groups). Q&A sites (Quora, StackExchange, even Reddit AMAs). Keyword research tools.
You can still do it. But it’s better to go straight to the source. Simply visit Google, search for the most queries, even one-word broad ones, in your industry, and then search for the questions offered there.
Before PAAs, highlights were the next big thing. But in 2022 there were 10 times more PAAs than snippets on Google, and featured snippets often led to non-click searches. You often need outline markup to categorize fragments, which means extra work.
PAAs are different. They can increase traffic to previously less prominent sites (including my almost-dormant SEO blog). I won a PAA for my Twitter Resources post that neatly listed the pros and cons of Twitter in a side table.
You can do the same. All you need to do is provide a useful resource in common sense text format (tables, lists) and there you go.
Check out Jason Barnard’s article, Google Brand SERPs: Why You Should Dominate People Also Ask, for a deep dive into PAAs.
Take Google’s advice with a grain of salt, but don’t ignore it
We don’t want to follow Google and blindly believe everything they say. They may omit things they don’t want you to focus on or use language that is difficult to decipher. Read between the lines when it comes to official announcements and documentation.
Implement sustainable SEO tactics that work in the long run. They may not be as flashy as the latest AI-powered tool, but they’ll help you stay in business for years to come.
The views expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
[ad_2]
Source link




