Search Engine Optimization (SEO) poisoning. and malvertising has increased significantly as more people use search engines than ever before. SEO poisoning affects both individuals and businesses, but many are unaware of the security threat it poses.
This article will discuss SEO poisoning: how it works, detection and prevention mechanisms, and mitigation strategies.
Definition of SEO poisoning
SEO poisoning is a technique used by threat actors to increase the prominence of their malicious websites, making them appear more authentic to consumers. SEO poisoning tricks the human mind into thinking the top hits are the most credible and is very effective when people don’t look closely at the search results. This can lead to credential theft, malware infections, and financial loss.
Threat actors can even use specific types of SEO poisoning, such as spear-phishing, to target specific users, such as IT administrators. The technique allows attackers to target and tailor their attacks to specific audiences, making them harder to identify and defend against.
How SEO Poisoning Works
Malicious actors use various techniques to achieve SEO poisoning. A common method is typosquatting, which targets users who may open their browser and enter a website address that has an inadvertent typo or click a link with a misspelled URL. To take advantage of these minor user mistakes, attackers register domain names similar to legitimate ones.
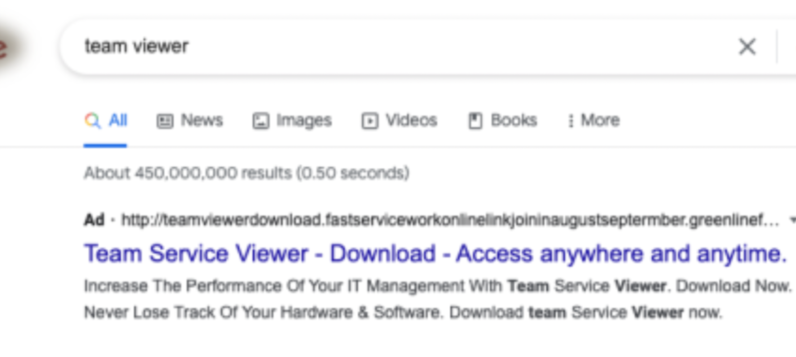
Let’s consider an example. A user searches for TeamViewer (a program that allows remote connection to computers) by typing “team viewer” into its search bar. The user may reach the first result without looking too closely at the URL and be redirected to a fake website where they are asked to download files infected with malware.
Typosquatting domains tend to appear at the top of search results, making users likely to click on them.
Example of seo poisoning in a search engine result
Blackhat SEO
Blackhat SEO refers to unethical tactics used by website owners to increase search engine rankings, such as keyword stuffing, cloaking, manipulating search rankings, and using networks to ‘private links.
Keyword stuffing: Include irrelevant keywords in a web page’s text, meta tags, or other parts of the website to trick search engine algorithms into giving the website a higher ranking.
cover up: Presenting search engine crawlers with material different from what is shown to the user when the link is clicked. This method influences search engine rankings by showing favorable information to crawlers while showing irrelevant content to users.
Manipulation of search ranking: Artificially increasing a website’s click-through rate to increase its search engine rankings. This method uses robots or humans to search for keywords and generate fake clicks for a particular website.
Use of private link networks: Creating a group of unrelated websites and connecting them together, resulting in a network of backlinks to a main website. This is also a method of artificially boosting search engine results as it seeks to mimic legitimate link building practices.
Recent SEO poisoning campaigns
Several incidents occurred in January 2023 fake installers distributed through SEO poisoning or malicious advertising. Cybercriminals used poisoned Google Ads to release Python-based malware that would steal information such as browser passwords and cryptocurrency wallets.
Fake installers and SEO poisoning remain popular with criminals to deliver malware. For example, recent incidents involved fake installers for OBS Studio or Notepad++ that loaded malware to steal sensitive information.
How to spot SEO poisoning
Identifying SEO poisoning can be difficult, but organizations can better prepare by implementing typosquatting detection procedures using digital risk monitoring tools. As soon as a new similar URL is created, DRM can inform security personnel with information about the owner.
Another method of detecting malicious URLs is through the use of Indicators of Commitment (IOC). IOC lists containing URLs can provide evidence of suspicious website behavior, anomalous search engine rankings, phishing attempts, unexpected changes in website traffic, and suspicious content. Lists can be used as watchlists or blocklists for preemptive detection or blocking.
Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions are a good way to quickly detect IOCs by monitoring and logging user and customer history. EDR tools can perform forensic analysis and investigate all user activity during a breach to determine whether a malicious file entered the system. Security teams can detect and contain SEO poisoning attacks by evaluating these data points.
How to prevent SEO poisoning
Beyond monitoring methods, organizations can also take proactive steps to prevent SEO poisoning attacks.
Training and awareness on user safety
User security education and awareness is critical to combating SEO poisoning attempts. Organizations can reduce the chances of falling victim to these attacks by training staff on safe browsing practices, phishing awareness, and effective endpoint security measures.
Internal security posture
Implementing a strong internal security posture and blocking known malicious sites can help prevent SEO poisoning attempts. Organizations can reduce the risk of employees visiting dangerous websites by frequently updating security software and establishing rigorous web filtering procedures.
Disclosure of abnormal SEO results
Periodic disclosure of abnormal SEO results to your security team allows for quick identification and response to any SEO manipulation attempts. It can also help ensure that the business can proactively protect its search engine ranking and online reputation.
How to mitigate SEO poisoning
To reduce the risk of SEO poisoning attacks, organizations can use typosquatting detection tools like CrowdStrike Falcon Intelligence Recon to identify if someone else is already using a variation of their domain.

CrowdStrike Global Threat Report 2023
The Global Threat Report 2023 highlights some of the world’s most prolific and advanced cyber threat actors. These include nation-state adversaries, eCrime and hacktivists. Read about the most advanced and dangerous cybercriminals out there.
Download now
Conclusion
This article discussed SEO poisoning, a technique cybercriminals use to distribute malware, steal credentials, and engage in illegal activities. Individuals and businesses must be aware of the dangers and take appropriate measures to protect themselves, such as conducting regular security assessments, educating staff and customers, and implementing endpoint detection and response systems.
CrowdStrike Falcon Insight XDR is an endpoint detection and response system that includes real-time response, allowing security teams to detect SEO poisoning instantly. To get started, check out the CrowdStrike Falcon free trial.
[ad_2]
Source link




