In today’s technology landscape, there is too much content to consume and too little time to do it. Having a well-developed website is not enough to stand out from the crowded online space.
video of the day
Innocn 48Q1V – Ultimate gaming immersion in this 48″ monster. The Innocn 48Q1V is one of the biggest, fastest, and best-sounding gaming monitors you can buy in 2023.
Fortunately, there are simple techniques you can follow to improve your website’s rankings and search engine exposure. Learn all about these practices and how you can drive organic traffic to your sites.
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a process that gives your content the best chance of being promoted by search engines. There are several techniques you can use to make sure your content is clean, of good quality, and presents well to search engine indexers. Follow them closely and you should be able to increase the quality and quantity of website traffic.
As a developer, your focus is typically on creating and managing the structure and functionality of your site. However, understanding SEO should also be part of your skill set, for many reasons:
SEO techniques help your website rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs), resulting in more traffic. Making sure your site uses relevant keywords or phrases means it’s more likely to reach your target audience. Implementing SEO improves the overall user experience, from page speed to responsiveness and mobile-friendliness. SEO efforts can generate long-term benefits. Search traffic is free, unlike paid advertising which stops generating traffic when you stop paying.
1. Write semantic HTML
When thinking about semantic markup, consider how you should structure your web page. This involves using precise HTML elements for the information you want to convey.
For example,
You should also pay attention to the hierarchy of headings. use H1 – H6 elements appropriately, to represent your document hierarchy. This allows search engines to better understand how you have organized your content and what is its order of importance. Semantic HTML is good for SEO as it improves accessibility and puts your website higher in the rankings.
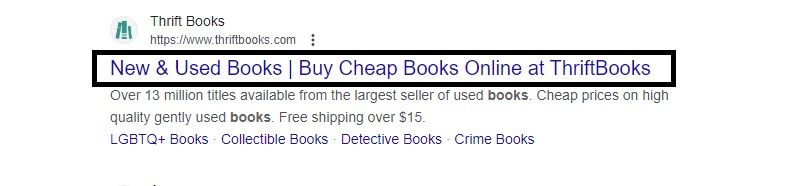
The title element is one of the first things you’ll discover when learning HTML. Title tags are important signals that help search engines understand what your website is about. They are one of the most important factors affecting the ranking of your pages in search results. Here is an example of how to implement a title tag in Google.
This image shows a top search result for the search “buy books online”. The highlighted text is a title tag, which you can add to your HTML page section like this:
<title>Title of your pagetitle>
Here are some things to keep in mind when writing a headline:
Include main keywords relevant to the website content. This will help search engines better understand what the website is about. One of the common mistakes you can make is keyword stuffing, including unrelated or simply too many keywords. One keyword is enough; place it closer to the beginning for better impact. When it comes to title length, there are two things to consider: the number of characters and the total width in pixels. Search engines may only display the first 50-60 characters of your title or the first 600 pixels. You don’t always have to count every pixel, just keep in mind that the beginning of your title may be more valuable than the end. Include your brand in the title. Be creative and use unique words.
It’s not enough to use title tags. Optimizing your title tags with relevant keywords, appropriate length and creative words helps a lot in SEO.
Meta descriptions summarize the content of a web page. This preview invites users to click through to your website. Meta descriptions are important features of SERPs. If you don’t add meta descriptions, Google will take topics from your content to replace them as meta descriptions. The result may not be very accurate and may not contain the catchy words you need to attract users to your web page.
Here is an example meta description:
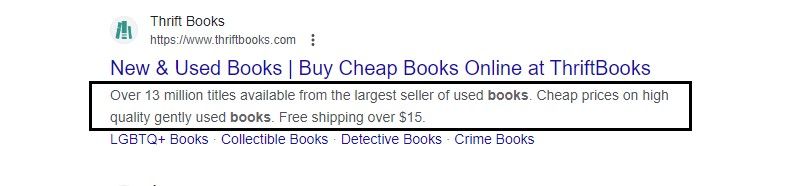
This image highlights a website’s meta description, which is easy to define in HTML. Here is an example description of a page about technology books:
>
<html lang=“in”>
<none>
<goal character set=“UTF-8”>
<goal first name=“lookout” content=“width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0”>
<link relative=“style sheet” href=“style.css”>
<title>Technology Books Online – Explore the best collection of technology bookstitle>
<goal first name=“description” content=“Discover high-quality tech books at Tech Books Online. Explore programming languages, cutting-edge technology, and more. Start your tech literacy journey now!”>
none>
…
html>
There are a few important points to keep in mind when writing meta descriptions:
Aim for a length of less than 150 characters. This is because most search engines only display the first 155-160 characters of a meta description in search results, cutting off anything else. Keywords and Catchy Lines – This involves using relevant keywords in the first few sentences as well as a strong hook to get readers to click through to the page. Make sure your description is concise, unique and includes a clear call to action.
Meta descriptions don’t directly affect search engine rankings, but a good meta description makes it more likely that people will visit your website from a set of search results.
4. Optimize URLs
Your site URLs should be descriptive and clear to both visitors and search engines. A poorly structured URL can hurt your website’s ranking. Many search engines highlight URLs quite prominently:
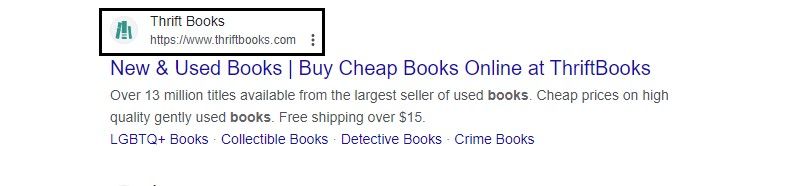
A good URL, with a clean structure, should:
Avoid long and unnecessary session IDs and other parameters. Distinguishes between uppercase and lowercase letters; try using hyphens to separate words instead of underscores or camel caps. Use only lowercase letters. Be precise.
Well-structured, descriptive, free of unnecessary parameters and accurate URLs are essential to maintaining a good website ranking.
5. Ensure mobile compatibility
People access websites more on mobile phones than on desktop computers, making mobile-friendliness a very important aspect of SEO. As a result, search engines now reward mobile-friendly websites in their rankings, while penalizing those that are not. You can improve the mobile friendliness of your websites using CSS media queries and many other methods.
@media (maximum width: 767 pixels) {
}
@media (minimum width: 768 pixels) i (maximum width: 1199 pixels) {
}
@media (minimum width: 1200 pixels) {
}
Using CSS techniques to create mobile-friendly websites that adapt to different screen sizes gives your website a good position in the SERPs.
6. Optimize images
Because there are many websites, there are many images. Website ranking is closely tied to images as they improve website performance, user experience and SEO. You can optimize images by compressing them and using alt attributes (sometimes called “alt tags”).
Alt attributes help search engines associate images with web page content. This allows search engines to properly index them within their search results. You should write alternative attributes for an audience that may not be able to see the images. This audience includes those with visual impairments, as well as search engines that do not analyze image content.
Be sure to accurately describe your images and include relevant keywords. Here’s an example of an image and how you can use an alt attribute to optimize it in HTML:
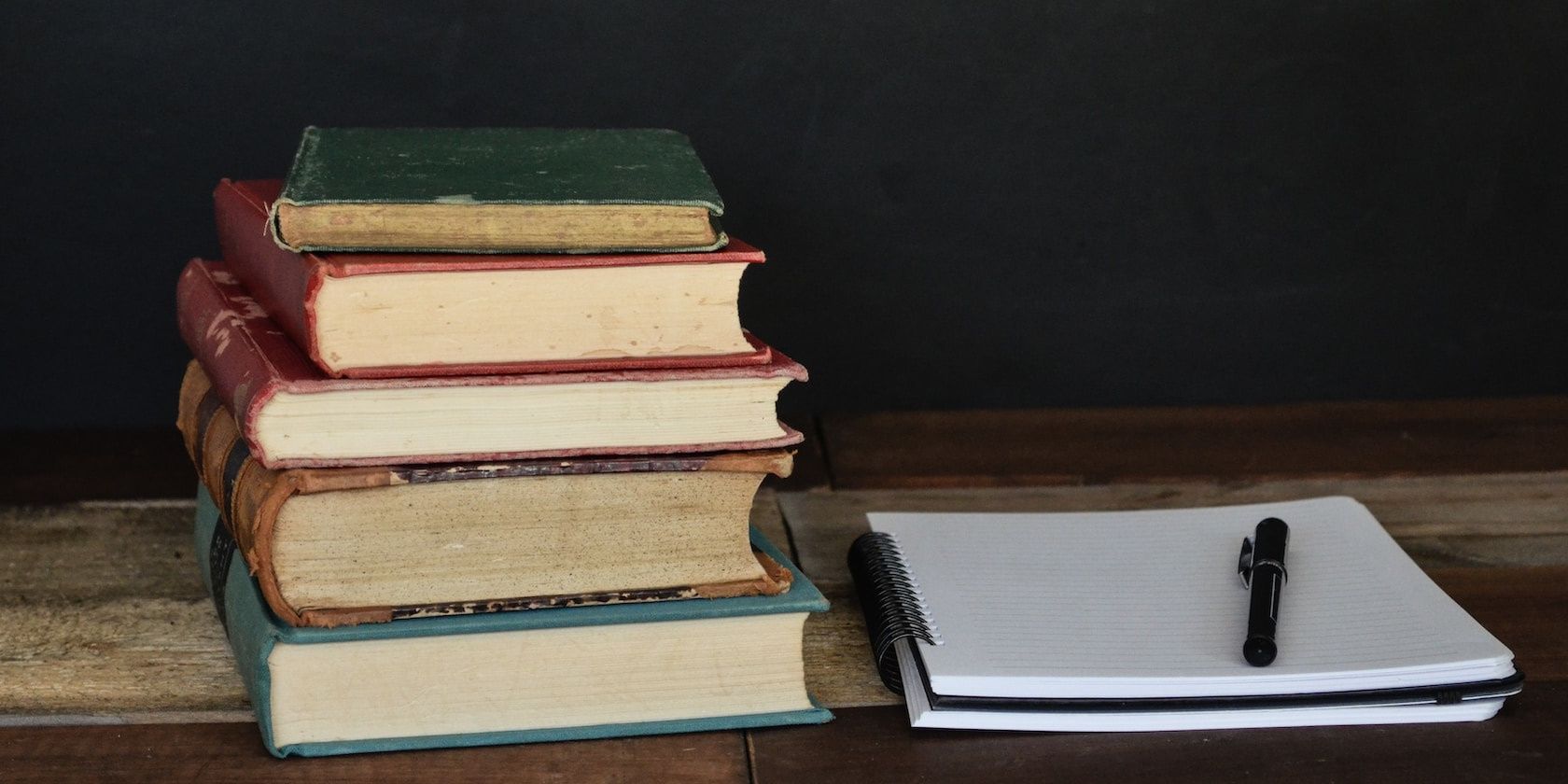

<image src=“books.jpeg”
alt=”Pile of books with a black pen resting on a notepad, placed on a wooden table.”>
When it comes to SEO, the faster the page loads, the better. Your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files may be small, but once you upload images with large sizes, it will slow down your website. The best practice is to compress all the images on your website, which you can do in many different ways. Using an online tool to compress images is just one option.
7. Improve page speed
The faster your website loads, the better. When a page takes too long to load, users become disinterested and click away. Fast loading websites improve the user experience and tend to have higher engagement and SEO ranking. There are a few techniques that can help you as a developer optimize your page speed, some of which are:
Reduce images using efficient file formats and compression. Minify and compress your website’s HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files. This involves removing unnecessary characters such as spaces and comments; an automated tool can help. Use a content delivery network (CDN). A CDN is a network of servers that distributes your website’s content around the world, serving users from the closest server.
Remember, the lighter or optimized your website is, in terms of file size, the faster it loads.
Unlock your website’s potential with SEO
By adopting these SEO best practices as part of your development process, you’ll be in a better position to create a website that not only ranks high in the SERPs, but also offers an exceptional user experience.
Remember that SEO is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring and analysis to keep up with search engine algorithms.
[ad_2]
Source link




