Tl;dr: Phishing takes advantage of the trust we have in search engines and the convenience of searching for something instead of remembering the domain. The following piece describes what search engine phishing attacks can look like and how Coinbase users can avoid them.
By the Coinbase Security Team
How do you log in to Coinbase? If you’re like many people, open your favorite browser and type “Coinbase” or “Coinbase login” into the address bar. Expect results like this:
But sometimes you can get results like this:
The second set of screenshots shows an example of phishing links. This is called search engine phishing and has become a trend for attackers targeting Coinbase accounts.
When most people think of phishing, email or SMS phishing comes to mind. However, fishing can take many forms. Phishing takes advantage of the trust we have in search engines and the convenience of searching for something instead of remembering the domain.
We all do, but this opens us up to potential search engine phishing attacks if we’re not diligent about checking our links and protecting ourselves online. Here are some tips to prevent this from happening to you:
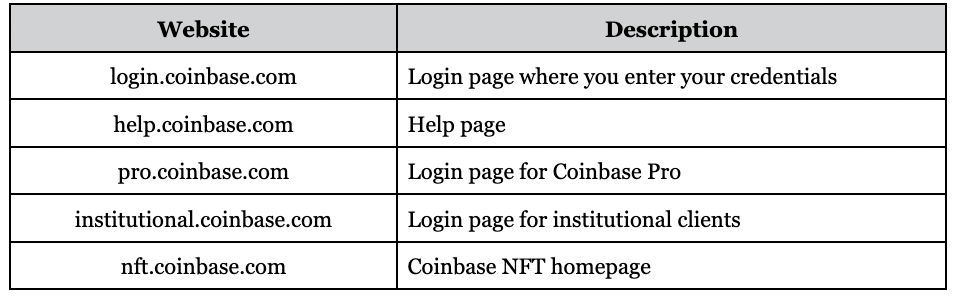
Coinbase uses a uniform naming convention for our websites and pages. The convention follows this pattern: [page].coinbase.com. For example, here are some of our pages:
One way to avoid this type of scam is to bookmark the previous Coinbase pages you frequent. Bookmarking eliminates the need to search or manually type in a domain name. Here’s a quick one tutorial on how to create bookmarks in the most popular browsers.
It takes a fair amount of work for anyone to get their website to rank high in search engine results. This is called Search Engine Optimization (SEO), which is the process of improving search engine traffic to a website. Some website services, such as Google Sites and Microsoft Azure, offer built-in SEO functionality.
As you can see in the screenshots above, attackers tend to exploit website services like Google Sites and Microsoft Azure, creating a false sense of trust in the phishing link. Naming conventions can follow a pattern such as one of the following:
sites.google.com/[phishingpage].how
[phishingpage].azurewebsites.net
These phishing websites will usually redirect to another phishing page after a victim clicks on a button on the site. The redirect will take the victim to a second phishing page where the actual phishing attack takes place. Using a second phishing site is a way for attackers to protect the first phishing site and maintain their SEO ranking. Therefore, be aware of redirects as an indication that you may be visiting a phishing website. A typical flow might look like this:
Here are some indicators you can look for to protect yourself from search engine phishing:
The search result naming convention follows this pattern: [page].coinbase.com? If not, it’s likely a phishing page.When you click on a search result, are you redirected to a website with a different domain than you expected? If so, it’s likely a phishing page.When you click on the search result, does the website look different from the last time you logged into Coinbase? If so, it could be a phishing page using an older version of our website theme.When you visit the website from the search results and click a button, are you redirected to a website with a different domain than the first page? If so, it’s likely a phishing page.After entering your credentials, are you being asked to call Coinbase for some kind of error? Does a live chat box automatically open? This tactic is commonly combined with phishing attacks and is known as a “support scam” attack.
Here’s an example of what a scam error might look like and a live chat box that might follow the error:
Remember, think before you click! Our US support phone number is 1–888–908–7930 and you can find other ways to contact us at help.coinbase.com. If you suspect activity on a “Coinbase” website, please go to our help page and start a conversation with our support team there.
We are constantly monitoring the Internet to identify phishing domains and remove them, but we need your help. Help us by reporting any suspicious domains to security@coinbase.com.
[ad_2]
Source link




