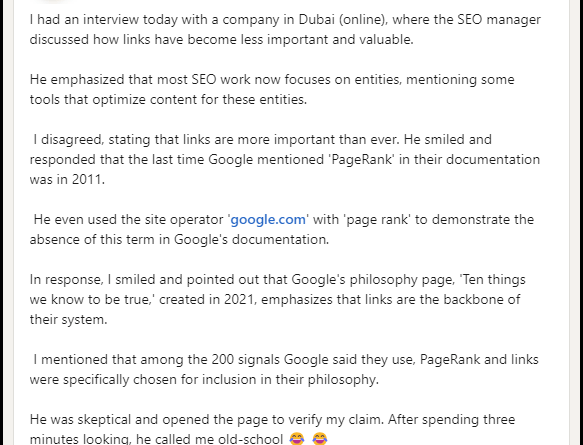
SEO today is more complex and challenging than at any other point.
Once upon a time, not too long ago, links were the most important thing in SEO.
But is this still true?
This article will examine the importance of link SEO today. It will include various perspectives within the industry, analyze empirical evidence, and consider recent statements and updates from Google regarding the role of links in its ranking algorithms.
Inbound Links and SEO: Confusion in Today’s Landscape
Links matter. The volume and quality of external links to a web page can influence its search ranking.
Beyond the number of links, other factors that play a role include:
Link diversity (are your links coming from multiple sites?). membership quality authority
Technical aspects and Google’s preference for editorial (non-paid) links have more of an impact on effectiveness.
Links build PageRank, which helps raise keyword rankings. Although Google no longer displays PageRank publicly, it still influences its algorithm.
How much? Opinions vary. Some believe that PageRank is crucial, while others think that its importance is practically dead.
Just check out this LinkedIn post:
These posts can lead to interesting discussions that surface interesting opinions:
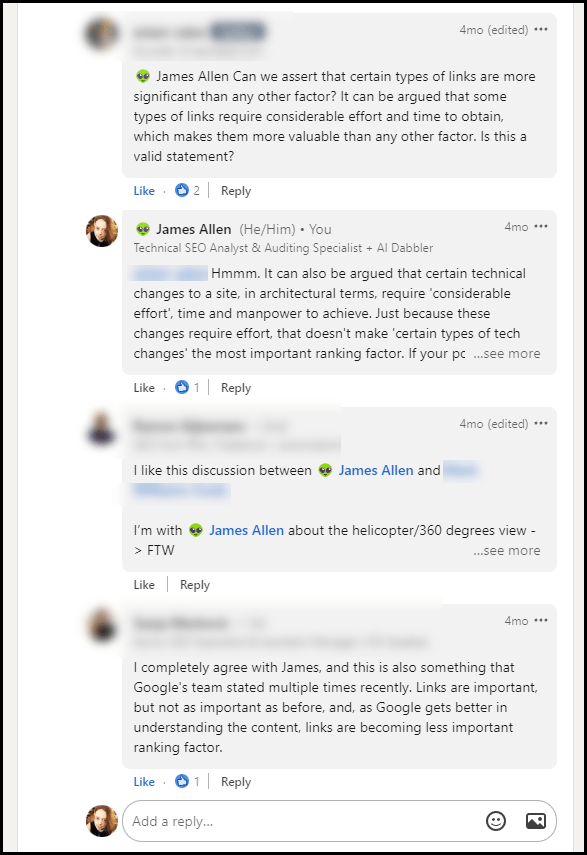
Opinions on the importance of links vary widely, leaving many confused.
If you are among the confused, know that you are not alone.
So are links as crucial as marketers say? Or are the links an industry scam costing thousands of unnecessary links?
The truth, as is often the case, lies somewhere in between.
Let’s examine these perspectives further and measure them against the facts.
Statements and updates from Google
Before proceeding, it’s probably wise to check Google’s recent comments.
Let’s start with comments from Gary Illyes, a trends analyst for Google webmasters, from September, as reported here on Search Engine Land:
“I think they [links] they are important, but I think people overestimate the importance of links. I don’t agree that it’s in the top three. It hasn’t happened for a long time.”
Then, in March, Google released an update to its spam policy, removing the word “important” in reference to links as a ranking factor. This change coincided with the March 2024 core algorithm update.
In April, there was a bit of a storm when Illyes pointed it out links were less important in a search conference:
“We need very few links to rank pages… We’ve made links less important over the years.”
John Mueller, a Google search advocate, also made these comments:
“My recommendation would be not to focus so much on the absolute link count. There are many ways that search engines can discover websites, such as with sitemaps. There are more important things for websites today up to date, and focusing too much on links will often waste your time doing things that don’t make your website better overall.
Some parts of Google’s documentation still mention links and PageRank as core aspects of their ranking systems.
Within their documentationGoogle claims that PageRank is:
“One of our core ranking systems used when Google was launched. The curious can learn more by reading the original PageRank research paper and patent. The way PageRank works has evolved a lot since then and continues to be part of our basic classification systems”.
So, even if Google is reducing the prominence of link data within its ranking algorithms, it looks like it will be a gradual sunset.
And that’s what Google is philosophy page says:
“We assess the importance of each web page using more than 200 signals and a variety of techniques, including our proprietary PageRank™ algorithm, which analyzes which sites have been ‘voted’ as the best sources of information by other pages on the web. A as the web gets bigger, this approach gets better, as each new site is another point of information and another vote to count.”
This suggests that links and PageRank are still important in 2024. However, if you read further:
“We never manipulate rankings to put our partners higher in our search results, and no one can buy a better PageRank. Our users trust our objectivity, and no short-term gain could ever justify breaking that trust.”
The statement that “no one can buy a better PageRank” indicates that Google aggressively defends this part of its ranking algorithm.
It also suggests that Google believes, or wants us to believe, that paid link building services are ineffective. If these services were effective, Google would not be able to claim that no one can buy a better PageRank.
This is not to say that links are not important. But Google invests heavily in making simple link building strategies ineffective.
Despite Google’s efforts to reduce link dependency and prevent backlink exploitation, the SEO industry still promotes link building as a valid tactic. The industry continues to generate business and educate those they consider uninformed.
These practices will persist unless Google makes sweeping changes to its ranking algorithms and clearly communicates them to the industry.
Google aims to move away from links to better rank content, but what could replace PageRank?
For now, nothing.
However, with Google’s AI capabilities, that could change.
If Google can evaluate the usefulness of content directly without external links, it will no longer need to rank web pages. Instead, answering search queries will become an exercise in AI-powered technical content extraction and emergence.
This change seems inevitable.
Empirical evidence and studies
The key question to ask when it comes to your SEO efforts is, “Are the links working right now?”
Let’s see the findings of Ahrefs, Backlinko i MonsterInsights:
Study 1: Ahrefs backlink statistics and findings
Ahrefs, a cloud-based platform for backlink analysis, keyword indexing, content optimization and technical SEO auditing, updated its SEO statistics for 2024 on 18 of March
Ahrefs found a positive correlation between the number of sites linking to a page and that page’s ranking and SEO traffic performance. Most top ranking pages gain 5% to 14% more backlinks per month.
Many other Ahrefs statistics refer to publishers like Authority Hacker and include survey-based data.
Study 2: Backlinko Search Ranking Results
“A site’s overall link authority (as measured by Ahrefs Domain Rating) correlates strongly with higher rankings,” according to a Backlinko study, updated March 24.
Google does not use SEO tool scores in its algorithms, but still uses PageRank. Ahrefs Domain Rating is designed to simulate PageRank, so a correlation is expected if Ahrefs is accurate.
Backlinko’s study also said:
“Pages with a lot of backlinks rank higher than pages that don’t have as many backlinks. In fact, the #1 result on Google has an average of 3.8 times more backlinks than positions number 2-10”.
However, correlation does not imply causation. High rankings can make a page more visible, resulting in more backlinks and citations. Even so, the correlation between link authority and higher rankings is strong.
“We found no correlation between page load speed (as measured by Alexa) and Google’s first page ranking.”
The above point is a bit misleading. Google does not adjust rankings based on Alexa page speed scores. Instead, they use Core Web Vitals to evaluate page performance. Therefore, this claim may be based on poor input data.
Let’s move on to the next point:
“Getting backlinks from several different sites seems to be important for SEO. We found that the number of domains linking to a page correlated with rankings.”
The importance of link diversity is generally accepted in the search community.
Study 3: Monster Insights Ranking Factor Results
Monster Insights, a WordPress plugin provider, determined that backlinks “have a large influence on Google’s ranking algorithm,” in January.
Monster Insights concluded that sites with higher volumes of backlinks tend to achieve higher Google ranking positions (on average):
“Overall, backlinks from high-authority websites are more valuable and will increase your ranking more than links from lower-rated sites. Acquiring these links sends a signal to Google that your content it’s reliable, as other high-quality websites vouch for it.”
Make sense of link data and associated claims
While most studies show a correlation between links, rankings, and search traffic, they do not address causation.
Do links make pages rank higher or do high ranking pages attract more links?
This has been an important debate in SEO for over a decade.
Some have had success with link building, while others have seen no results or even received a manual action from Google.
I trust the Ahrefs study more because it provides tools and data without selling link building services, reducing bias. They have a massive index of over 14 billion live backlinks.
Understanding the role of backlinks in 2024
Your main point is that links are still important now.
However, traditional link building, which often produces poor quality links, has long been ineffective.
Success requires creative ideas and real-world events that get high-level editorial coverage.
Don’t “build” links. Earn and attract links. Producing links is not as simple as stacking blocks.
Although backlinks are becoming less important, they are still an important part of SEO.
Taking a holistic, quality-focused approach to link acquisition and broader SEO strategies will likely yield the best results in this changing landscape.
The opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
[ad_2]
Source link




