Videos are an organic search opportunity. They can appear in Google video carousels and improve a page’s ranking when inserted.
Here’s how to optimize your videos on-site.
Onsite Video SEO
1. Guarantee relevance. A video should contribute to the purpose of the page. Don’t add videos just for search engine optimization. Put visitors first. Relevant and useful videos drive engagement and send positive signals to Google.
Keyword research, the foundation of all SEO, applies to videos. Search Google for intuitive words and phrases. A query that produces video carousels is worth optimizing.
2. Emphasize quality. Make sure your video is clear, organized and to the point. Ask friends, colleagues and target buyers to review it.
Study Google’s carousel videos to gauge what’s available for a given query.
3. Use an attractive thumbnail. Video thumbnails appear in search results in carousels and rich video snippets. A video’s thumbnail is also what people see on the page before playing it.
Therefore, thumbnails are important for organic clicks and page engagement. Create a unique image that reflects the intent of the video.
4. Upload to YouTube. Video hosting options include your own site and third-party platforms (free and premium). But YouTube is the best choice for organic ranking because of Google’s ownership of this site.
When uploading to YouTube, use the custom thumbnail above at 1280 x 720 pixels with a minimum width of 640. It’s important to add explanatory content, which will help Google categorize this video and rank it higher. Next, confirm that Google can generate a transcript of the video. A transcript indicates that Google understands the content.
When you upload a video to YouTube, you confirm that Google can generate a transcript.
5. Use structured data. A video must be viewable and playable on a page to be able to generate rich video snippets. Using the YouTube video embedded code achieve both easily.
When embedding YouTube videos, add ?rel=0 to the video URL inside the code to prevent Google from suggesting competitors. With this string present, YouTube will suggest your own videos.
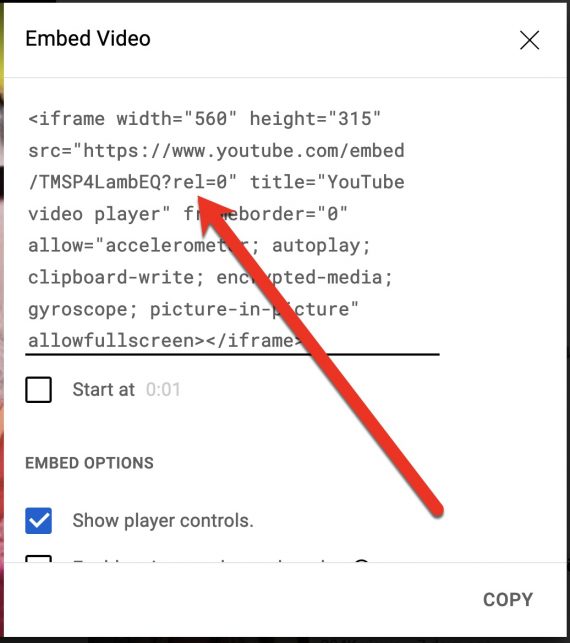
Adding ?rel=0 to a YouTube embed code prevents Google from suggesting competitors’ videos.
Also consider using structured data from Schema.org when embedding your video. It’s not necessary for rich video snippets, but it won’t hurt. Videoschema.com offers a free generator from Schema.org.
Using YouTube as a hosting platform means that Google probably pulls all the metadata (author, publication date, description) without the structured data. But it certainly includes Schema.org markup (and a transcript) when not hosted on YouTube.
6. Lazy loading videos. Videos can slow down a page. Always lazy upload videos to ensure good ratings in Core Web Vitals.
There are solutions to implement lazy loading depending on your platform. WPbeginner offers a workaround for WordPress that also adds ?rel=0 to the embed code. A site called Section Design has a tutorial for Shopify. Wix claims to provide lazy loading by default.
Otherwise, check with your platform provider.
7. Produce a video XML sitemap. An XML sitemap can link to all the videos on your site, increasing search engine discovery. Humans don’t see XML sitemaps.
Keep an eye on the “Video Pages” report in Search Console to make sure Google can access and index this content.
[ad_2]
Source link




