A critical vulnerability was discovered and fixed in the Better Search Replace plugin for WordPress, which has more than 1 million active website installations. Successful attacks can lead to arbitrary file deletion, recovery of sensitive data, and code execution.
Degree of severity of the vulnerability
The severity of vulnerabilities is scored on a point system with ratings described as low to critical:
Low 0.1-3.9 Medium 4.0-6.9 High 7.0-8.9 Critical 9.0-10.0
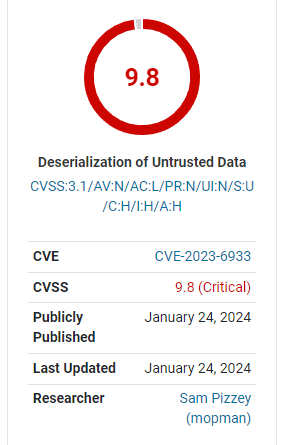
The severity of the vulnerability discovered in the Better Search Replace plugin is rated Critical, which is the highest level, with a score of 9.8 on the 1-10 severity scale.
Wordfence illustration
Better Search Replaces WordPress plugin
The plugin is developed by WP Engine, but was originally created by the developer company Delicious Brains which was acquired by WP Engine. Better Search Replace is a poplar WordPress tool that simplifies and automates the process of performing a search and replace task on a WordPress website database, which is useful in a site migration task or servers The plugin comes in a free and paid Pro version.
The plugin website lists the following features of the free version:
“Serialization support for all tables The ability to select specific tables The ability to run a “dry run” to see how many fields will be updated No server requirements other than a running installation of support for WordPress Multisite”
The paid Pro version has additional features such as the ability to track what has been changed, the ability to backup and import the database while the plugin is running, and expanded support.
The plugin’s popularity is due to its ease of use, usefulness, and history of being a trusted plugin.
PHP object injection vulnerability
A PHP object injection vulnerability, in the context of WordPress, occurs when a user-supplied input is not serialized insecurely. Deserialization is a process where string representations of objects are converted back into PHP objects.
The non-profit Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) provides an overview description of the PHP Object Injection vulnerability:
“PHP object injection is an application-level vulnerability that could allow an attacker to perform various types of malicious attacks, including code injection, SQL injection, path traversal, and application denial of service, according to the context
The vulnerability occurs when user-supplied input is not properly sanitized before being passed to the PHP unserialize() function. Because PHP allows object serialization, attackers could pass ad-hoc serialized strings to a vulnerable call to unserialize(), leading to arbitrary injection of PHP objects into the application scope.
To successfully exploit a PHP object injection vulnerability, two conditions must be met:
The application must have a class that implements a PHP magic method (such as __wakeup or __destruct) that can be used to perform malicious attacks or start a “POP chain”. All classes used during the attack must be declared when the vulnerable unserialize() is being called, otherwise automatic object loading for these classes must be supported.
If an attacker can load (inject) an entry to include a serialized object of their choice, they can execute arbitrary code or compromise the security of the website. As mentioned above, this type of vulnerability usually arises due to improper sanitization of user inputs. Sanitization is a standard process of verifying input data, so that only expected types of input are allowed, and unsafe input is rejected and blocked.
In the case of the Better Search Replace plugin, the vulnerability was exposed in the way it handled deserialization during search and replace operations. A critical security feature missing in this scenario was a POP chain—a series of linked classes and functions that an attacker can use to trigger malicious actions when an object is not serialized.
Although the Better Search Replace plugin did not include this string, the risk remained that if another plugin or theme installed on the same website contained a POP string, it could allow an attacker to launch attacks.
Wordfence describes the vulnerability:
“The Better Search Replace plugin for WordPress is vulnerable to PHP object injection in all versions up to and including 1.4.4 via untrusted input deserialization.
This makes it possible for unauthenticated attackers to inject a PHP object.
There is no POP string in the vulnerable plugin. If there is a POP chain through an additional plugin or theme installed on the target system, it could allow an attacker to delete arbitrary files, retrieve sensitive data, or execute code.”
In response to this discovery, WP Engine quickly addressed the issue. The changelog entry for the update to version 1.4.5, published on January 18, 2024, highlights the steps taken:
“Security: Deserializing an object during search and replace operations now passes ‘allowed_classes’ => false to prevent object instantiation and potentially executing malicious code stored in the database.”
This update followed Wordfence’s responsible disclosure of the vulnerability on December 18, 2023, which was followed by WP Engine’s development and testing of the fix.
What to do in response
Better Search Replace plugin users are requested to update to the latest version immediately to protect their websites from unwanted activities.
[ad_2]
Source link




