In the ever-evolving marketing landscape, the use of customer data has become more critical than ever. Customer data platforms (CDPs) have emerged as a game changer, which allows companies to harness the full potential of their customer data. With CDPs, organizations can unlock a wide range of use cases, each serving specific business needs. This article covers a CDP use case, its benefits, and how to implement them effectively for maximum impact.
Drag, Walk, Run: The Iterative Approach for a CDP Use Case
Before delving into a specific CDP use case, it is essential to emphasize the importance of the iterative approach. Often, organizations tend to get overwhelmed by the possibilities of a CDP and aim for complex solutions right from the start. Instead, adopting a “crawl, walk, run” approach can be very beneficial.
To get started, start small, perhaps tackling a simple use case and work your way up. This way, you can understand how CDP integrates into your existing systems and learn how to leverage its full potential incrementally.
How can you use the “drag, walk, run” approach?
Cart abandonment is a common CDP use case. Here is an example with the iterative “Crawl, walk, runapproach
Crawl: Identify customers who abandon their carts and track this data. Measure your cart abandonment rate and its impact on revenue. Start sending basic email reminders to encourage customers to complete their purchases. To activate this data, connect your CDP to your email marketing tool and potential audience cart abandoners.
Walk: As you gain experience, it’s time to dig deeper into the data. Analyze customer journey events that lead to cart abandonment. Segment your audience based on attributes like cart value, product categories, or purchase history. Create personalized email content for different segments. You can also incorporate SMS or app notifications to reach customers through multiple channels. Use plugins to automate these processes.
To run: Now, take cart abandonment prevention to the next level. Implement dynamic on-site personalization for cart abandoners. Use returner data to identify and engage customers who have previously abandoned carts. Leverage retargeting campaigns on social media platforms to re-engage cart abandoners. Continuously measure and refine your strategies for optimal results through A/B testing and data analysis.
What is a use case in a CDP?
A use case in a CDP has eight main pillars. Here’s how they can add value to your business.
1. measurement
Defining measurable goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial when developing a CDP use case. For example, in a cart abandonment use case, measurement might involve tracking abandonment rate, number of carts recovered, and increase in revenue.
2. Business value
To determine business value, you need to identify the direct impact the use case will have on your organization. In the context of cart abandonment, the business value is evident in the form of increased revenue through sales recovery and improved customer retention.
3. Activation
Activation refers to the action you take based on the data and insights provided by the CDP. In a cart abandonment use case, activation involves sending personalized offers or reminders to customers who have abandoned their cart. Activation strategies must be well defined and designed to achieve the objectives set in the measurement phase.
4. Connectors
Plugins are the bridges that connect your CDP with other tools and platforms. In the case of cart abandonment, you’ll need plugins to integrate your CDP with your email marketing platform, in-app or SMS notification tools, and potentially your e-commerce platform for tracking and recovery abandoned carts effectively.
5. Audiences
Understanding your target audience is crucial. In the context of cart abandonment, the audience would be those customers who have abandoned their shopping cart. These audiences can be further segmented based on attributes and behaviors to effectively tailor messages and offers.
6. Attributes
Attributes are the characteristics or data points that define your audience segments. In the cart abandonment use case, attributes can include the abandoned cart value, product categories within the cart, purchase history, and more. These attributes help you personalize your messages and offers.
7. Customer Travel Events
Customer journey events are specific actions or interactions customers take along their path to purchase. In cart abandonment, the key event is abandoning a cart. Understanding the events of the customer journey allows you to identify when and why potential customers leave.
8. Data sources
Data sources are the places where relevant data is collected. Data sources for the cart abandonment use case include your website, e-commerce platform, customer relationship management (CRM) system, and CDP. Data from these sources is used to track customer behavior, collect cart abandonment data, and trigger activation processes. It is important to emphasize the need for quality and consistency of data from these sources to ensure accurate results.
With these elements in mind, create a comprehensive framework for building a CDP use case that is well-defined, measurable, and aligned with your business goals.
This is how everything comes together in a frame.
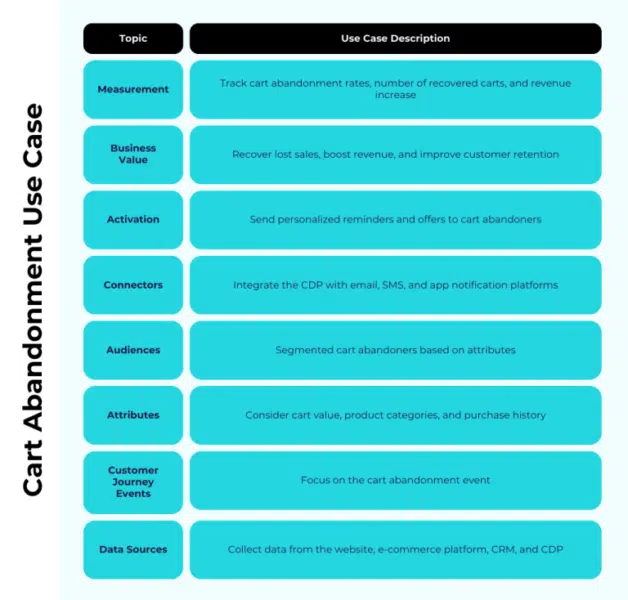
Examples of use cases associated with definitions
For a deeper look at the use cases, see the chart below with specific example definitions.
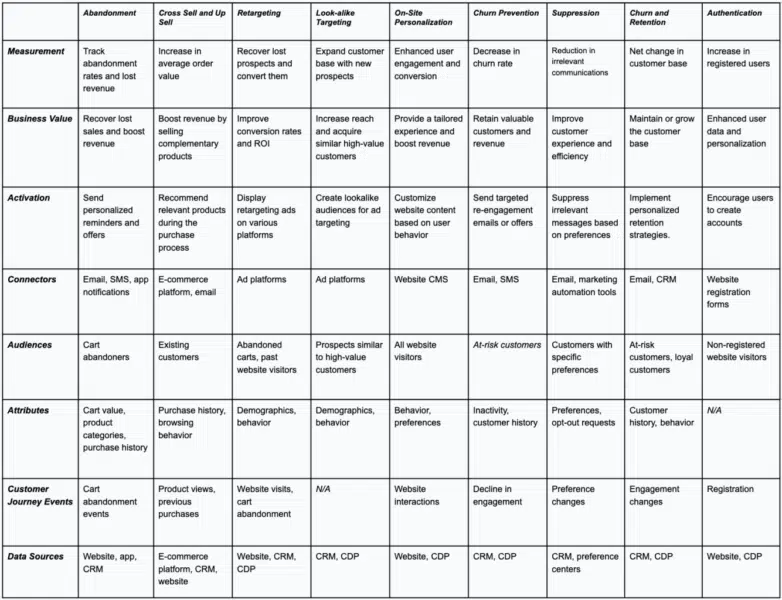
In conclusion, building a CDP use case involves careful planning. It’s important to focus on measurable goals, business impact, targeted activation strategies, data integration through plugins, well-defined audience segments, relevant attributes, customer journey events, and the data sources that drive the whole process When executed effectively, CDP use cases can significantly improve your marketing efforts, customer engagement, and overall business results.
Incorporating these CDP use cases into your marketing strategy can substantially improve customer engagement, retention and revenue. Remember that it is essential to start with simple implementations and gradually progress to more complex strategies. This approach ensures a smoother transition into the world of CDPs, allowing your organization to fully leverage the power of customer data. So, take the first step and start reaping the benefits of CDPs today. For more resources, explore this blog post, 5 Smart CDP Use Cases You’ll Want to Implement.
[ad_2]
Source link




