Generative AI doesn’t replace human creativity in marketing, but it can enhance it.
Shortly after OpenAI launched ChatGPT in November 2022, professionals in many industries became interested in generative AI. These tools work with foundational models, such as large language models (LLMs), that developers train on massive datasets. Marketers can use generative AI tools to automate and improve various tasks such as content creation, search engine optimization (SEO), and marketing targeting. However, they must also consider their risks, such as creating unoriginal content and data privacy concerns.
Explore four ways generative AI can help marketing teams increase productivity.
4 Ways Marketers Can Use Generative AI
Generative AI’s ability to write content and analyze large data sets makes it a suitable tool for various marketing use cases.
1. Generation of marketing copies
Marketing teams write a lot of content, such as ad copy, product descriptions, and blog articles, which can take considerable time and effort. However, generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT and Google Bard, allow marketers to speed up the writing process for both short and long-form content. For example, a copywriter can ask a generative AI tool to create 50 promotional tweets for their organization, and the tool does so almost instantly.
Marketers can use generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT, to generate social media posts.
A content marketer, on the other hand, could use generative AI to write comprehensive blog articles. The seller can ask the tool to write the article from scratch, or they can come up with an outline themselves and have the tool build it.
 ChatGPT can help marketers structure and write blog posts.
ChatGPT can help marketers structure and write blog posts.
Generative AI tools can write faster than humans, but marketing leaders may have concerns about content quality, and rightfully so. AI content can seem too formulaic or lack the right tone if marketers don’t use very specific prompts.
A skilled indicator engineer knows what information to include in his indicator to get quality results. For example, a life insurance ad needs a more serious tone than a pizza delivery app. Generative AI users need to refine their prompts when the tools generate content that falls short in terms of tone, style, or level of detail.
Free tools, such as ChatGPT and Bard, serve a general audience, but some paid tools, such as Jasper AI, are aimed specifically at marketers. These tools provide application templates to help users enter the appropriate information for different types of marketing copy.
2. SEO keyword research
To create a successful blog, content marketers should know what topics their audience cares about. Keyword research tools show the words, phrases, and questions that people are asking in search engines, which can help marketers identify blog post ideas that their audience wants to see. While many keyword research tools charge a monthly fee, marketers can use ChatGPT and Bard to conduct keyword research for free.
To get started, content marketers can ask the tool to list key topics related to their industry or audience. For example, a vendor for a sustainability reporting software company might ask the tool to list topics related to sustainability in business. The message then provides a high-level overview of what a blog post might cover, including key topics such as the circular economy and sustainable supply chains.
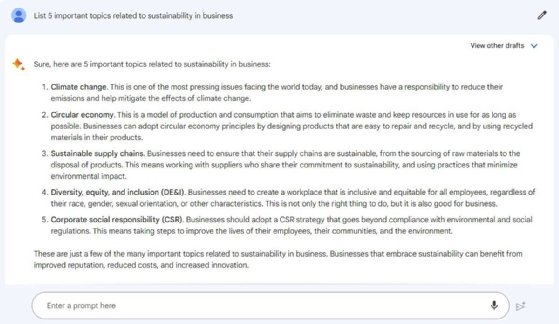 Organizations can use generative AI tools, such as Bard, to break topics into subtopics.
Organizations can use generative AI tools, such as Bard, to break topics into subtopics.
Marketers can then ask the tool to list keyword phrases for each topic. These keywords can help marketers create specific article topics and titles to attract the right audience to their website.
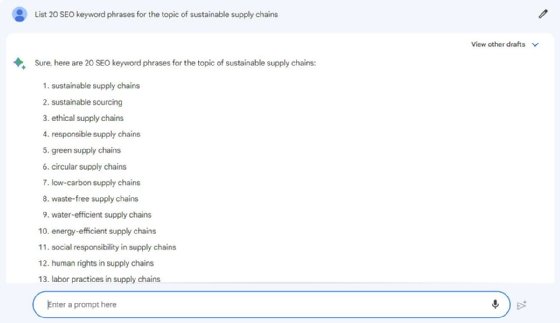 Marketers can use Bard to conduct SEO keyword research.
Marketers can use Bard to conduct SEO keyword research.
On the topic of sustainable supply chains, Bard could respond with keyword phrases such as “water-efficient supply chains” and “energy-efficient supply chains.” A content marketer can then use this information to write a blog post titled “5 Tips for Creating a More Water-Efficient Supply Chain” or “Best Practices for an Energy-Efficient Supply Chain.”
Bard learns from up-to-date information from the Internet, so marketers can use it to find trending keywords. The free version of ChatGPT, on the other hand, is based on data from September 2021 and earlier, so it may provide outdated results. However, the paid version of ChatGPT — ChatGPT Plus — integrates with the Bing search engine to access more up-to-date information.
If teams use Bard, ChatGPT, or ChatGPT Plus for keyword research, they can still use specialized SEO tools like Semrush and Ahrefs to verify search volume and cost-per-engagement information.
3. Segmentation and personalization of marketing
Marketing teams can improve market segmentation efforts by integrating a generative AI model with a data lake or customer data platform that contains a wealth of customer and prospect information. Customer segments (groupings based on common characteristics) help organizations understand their customers and deliver personalized experiences.
To create accurate segments, marketing teams must analyze a lot of data, which can take considerable time. However, generative AI can automate this process as it can analyze large amounts of data faster than a team of humans.
Generative AI’s underlying LLM can also enable marketers to use natural language to discover new customer segments. For example, a retail store salesperson integrating store data with a generative AI tool might ask the tool, “Which customers are most likely to show interest in our upcoming Father’s Day offer?” The tool could analyze all relevant customer data to generate a group of customers that the team may not have previously identified.
Marketers can then use generative AI to create personalized outreach for specific segments. For example, a seller of an online browsing store might ask a generative AI tool to write personalized email offers for specific segments.
 ChatGPT can tailor marketing copy for different audience segments.
ChatGPT can tailor marketing copy for different audience segments.
However, organizations should consult with risk management departments before adding generative AI to their segmentation process. Many governments regulate how organizations store and use customer data, such as personally identifiable information, so companies need to ensure that their generative AI tools work in accordance with these laws.
4. Creation of marketing surveys
Organizations conduct market research, often in the form of surveys, to understand consumer wants and needs. Marketing teams can use generative AI to quickly create a variety of marketing surveys, including segmentation, purchase process and customer loyalty surveys. This automation can save salespeople time and increase overall productivity.
 Generative AI tools can quickly create marketing surveys.
Generative AI tools can quickly create marketing surveys.
As with most AI-generated content, marketers may need to adjust their prompts or edit the tool’s output. However, generative AI can quickly provide marketers with a basic survey draft, which they can augment and edit as they see fit.
Risks of using generative AI in marketing
If marketing teams don’t edit AI-generated content or ensure data privacy, a generative AI tool can do more harm than good.
Common shortcomings of the technology include the following:
Low content quality. If marketers lack basic rapid engineering skills or use AI-generated copy without making their own edits, the copy can come across as unoriginal and shallow. A blog that lacks originality and depth may struggle to rank in search engines against competitors who use human writers. Content that doesn’t match the tone of the brand. Free generative AI tools don’t inherently understand how to write content according to a brand’s particular style or tone. Marketers must carefully formulate their leads and often refine them. They may also need to manually edit the results to match the tone of the brand. Limitations of knowledge. Generative AI tools may have a knowledge cutoff date. For example, the free version of ChatGPT doesn’t know about events that happened after September 2021 because OpenAI stopped training the tool’s foundational model in that month. Therefore, it cannot provide information about current events or trending SEO keywords. Data privacy issues. Not all generative AI tools have guardrails for storing sensitive data in compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. To avoid a data breach, organizations should consult with risk management teams before putting customer information into a generative AI tool. Potential for bias. Many LLMs that power AI tools were trained on a wide range of Internet content. Therefore, political or racial biases found on the Internet can creep into responses, which can damage a brand’s reputation.
Generative AI has the potential to automate various tasks and increase productivity, although the tools require marketers to altered their creative processes. To reap the benefits of generative AI, organizations can provide quick basic engineering training and guidelines to help marketers use the tool efficiently in their day-to-day activities.
[ad_2]
Source link




