The orca is back.
The latest Knowledge Graph update, released in March, continued the laser focus on personal entities. It appears that Google is looking for personal entities to which it can fully apply the EEAT’s credibility signals and aims to understand who is creating content and whether they are trustworthy.
In March, the number of Persona entities in the Knowledge Graph increased by 17%. By far the biggest growth in new people entities are people to whom Google is clearly able to apply EEAT credibility signals (researchers, writers, academics, journalists, etc.).
Reminder: The original Killer Whale update
The “Killer Whale” update started in July 2023 as a large EEAT update to the Knowledge Graph. The main takeaways from the July 2023 Knowledge Graph are that Google is doing three things:
Acceleration of Knowledge Vault growth (starting with Persona entities). Restructuring the Knowledge Vault to focus on subtitles important to user confidence to improve the application of EEAT signal algorithms. Quickly removing its reliance on Wikipedia and other human-curated sources.
We concluded that the March Killer Whale update was about person entities, focused on classification, and designed to promote EEAT-compliant subtitles.
The Knowledge Graph is Google’s machine-readable encyclopedia, memory, or black box. It has six verticals and this article focuses on the Knowledge Vault vertical.
The Knowledge Vault is where Google stores its “facts” about the world. The Killer Whale update increased the facts and entities in the Knowledge Vault to over 1.6 billion facts across 54 billion entities, according to Kalicube’s estimate.
What happened in the March 2024 Knowledge Graph update?
The number of Knowledge Vault entities increased by 7.23% in one day to 54 billion. Knowledge Vault personal entities increased by 17%. The biggest increase (+38%) occurred among Person entities with EEAT-compatible subtitles (researchers, writers, academics, journalists, etc.). The number of Knowledge Vault entries for Person entities using Wikipedia did not increase. This means that all new Person entities came from other trusted sources. Knowledge panels for personal entities increased by 2.55% and immediately appeared in the SERPs. This is a new phenomenon: the July 2023 Killer Whale update did not immediately affect knowledge panels in the SERPs. We estimate that 15% to 25% of all person entities in the Knowledge Vault are duplicates. 18% of the new personal entities tracked by Kalicube Pro that were added in the July 2023 Killer Whale update were removed from the Knowledge Vault prior to the Return of the Killer Whale update. When an entity achieves a place in the Knowledge Vault, there is a 1 in 5 chance that it will be removed, unless you continue to work with your entity and its EEAT credibility signals.
The Killer Whale update is about Persona entities
Between May 2020 and June 2023, the number of people entities in Google’s Knowledge Vault increased steadily, which is in line with the overall growth of Knowledge Vault.
In July 2023, the number of Persona entities tripled in just four days. In March, Google added an additional 17%.
In less than four years, between May 2020 and March 2024, the number of people entities in Google’s Knowledge Vault has increased 22-fold.
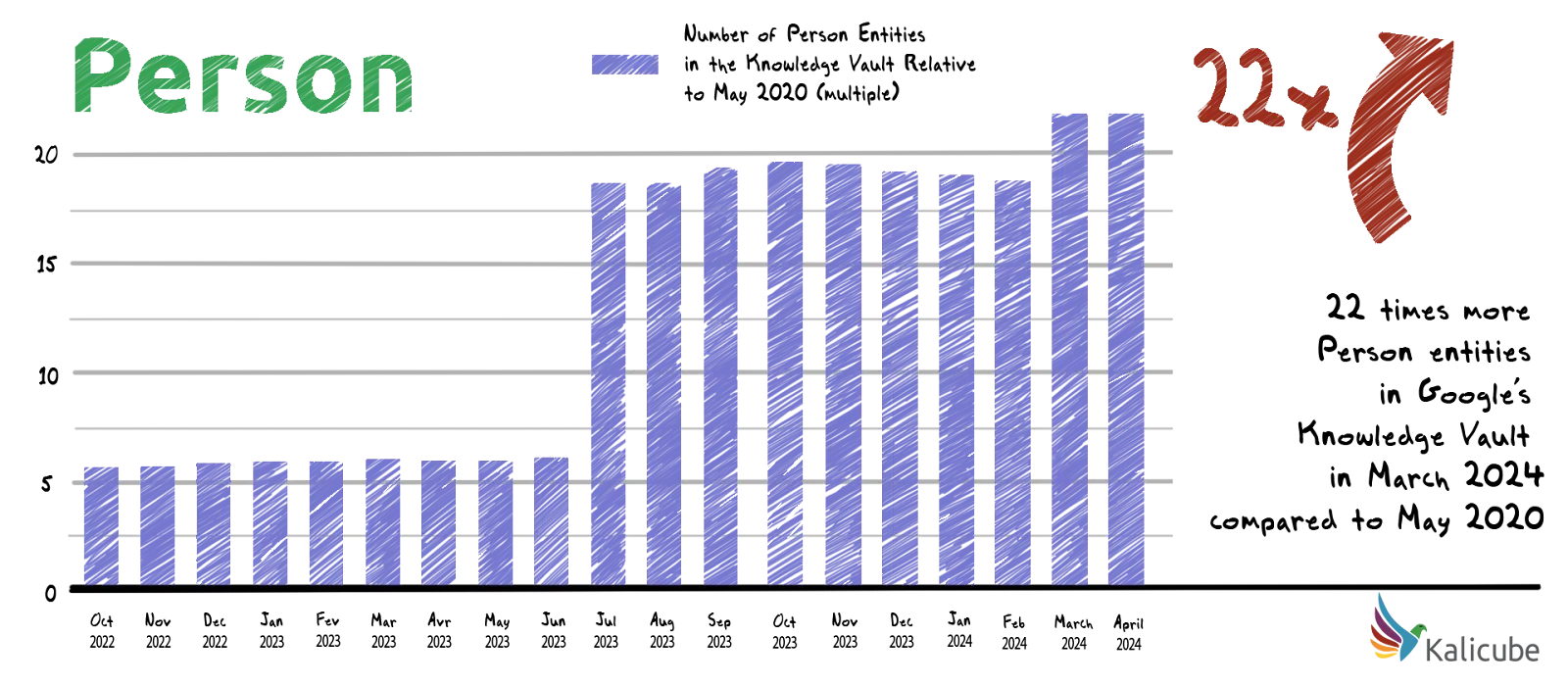
Between May 2020 and March 2024, the number of Corporation entities in the Google Knowledge Vault increased by 5. In the last year, however, the number of Corporation entities decreased by 1, 3%
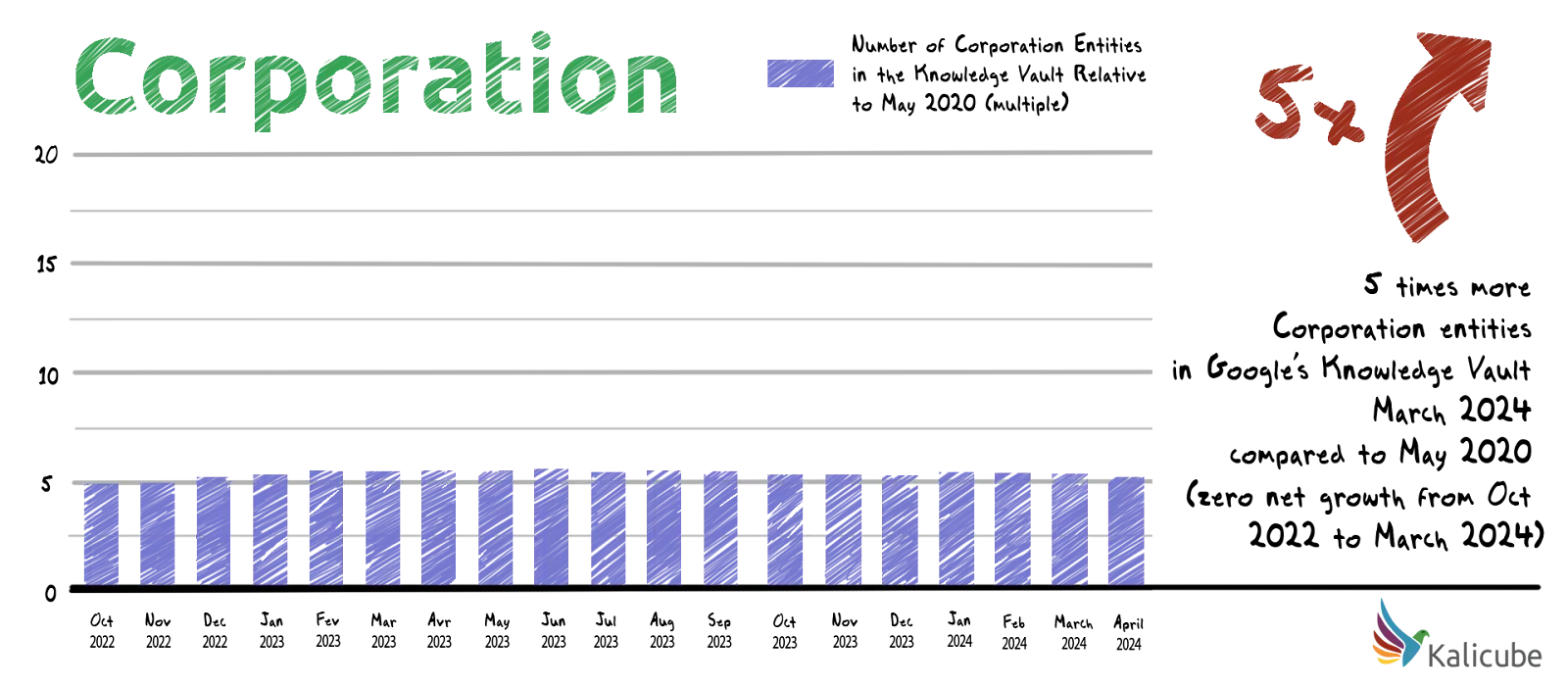
Google is focusing on person entities to an impressive degree, almost exclusively.
data: Kalicube Pro was tracking a core dataset of 21,872 people in 2020 and our analysis in this article uses this dataset. As of 2023, Kalicube Pro actively tracked over 50,000 corporations and 50,000 individuals.
Get the daily search newsletter marketers trust.
Why is Google looking for people to apply EEAT (NEEATT) signals to?
Google is looking for people. However, it specifically focuses on identifying people to whom it can apply EEAT signals because it wants to provide the most credible and reliable information to its audience.
We use NEEATT in the context of EEAT because our data shows that transparency and notability are essential to establishing a brand’s good faith.

The types of people Google focuses on are writers, authors, researchers, journalists, and analysts.
In March, the number of people to whom Google can apply EEAT signals increased by 38%.
You can ignore Wikipedia and other reference sources
Google added more than 10 billion entities to Knowledge Vault in four days in July 2023, then followed up with another 4 billion entities in a single day in March.
At this scale, it’s safe to assume that the Knowledge algorithms have now been “freed” from the shackles of the original set of trusted human-curated sites (Wikipedia only has 6 million articles in English).
This means that an entry to traditional trusted sources such as Wikipedia, Wikidata, IMDB, Crunchbase, Google Books, MusicBrainz, etc. is no longer necessary.
They are useful, but algorithms can now create entities in the Knowledge Vault without any of these sources if the information about the entity is clear, complete, and consistent across the web.

Anecdotally, I got this message on LinkedIn the other day
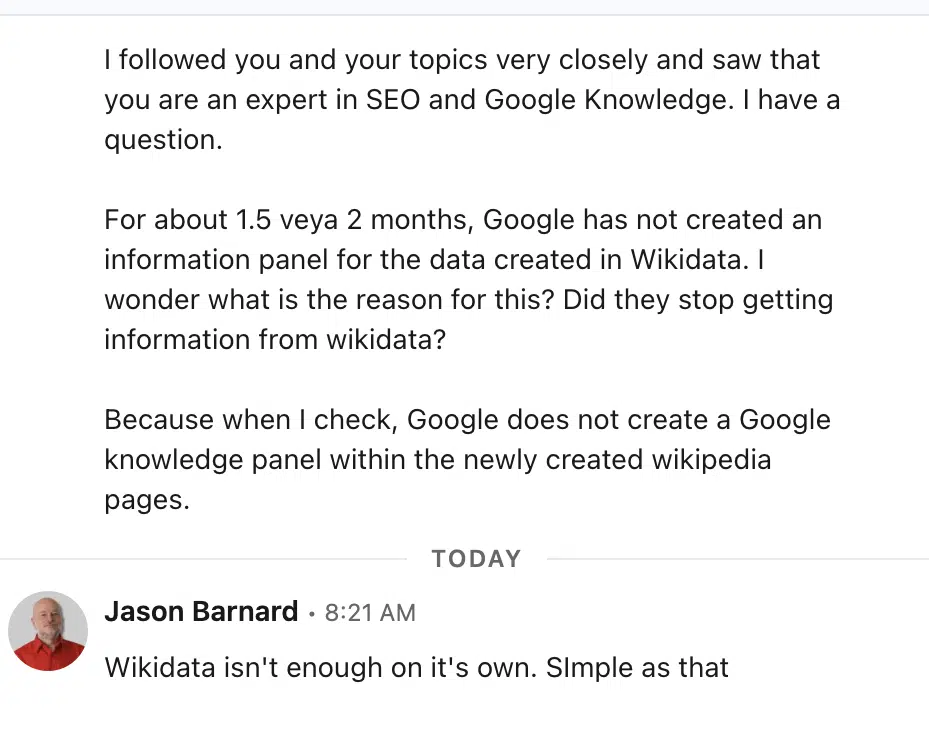
For a person entity, just auditing and clearing your fingerprint is enough to earn you a spot in Google’s Knowledge Vault and a Knowledge Panel. Anyone can get a knowledge panel.
Anyone with personal EEAT credibility that they want to leverage for their website or the content they create should work to establish a presence in the Knowledge Vault and a Knowledge Panel.
You’re Not Sure (Until You’re Not)
Almost one in five entities created in Knowledge Vault are deleted within a year, and the average lifetime is just under a year.
This should make you stop and think. Getting a spot in Google’s Knowledge Vault is just the first step in optimizing your entity. Trust and understanding are key to maintaining your site in the Knowledge Vault over time and keeping your Knowledge Panel in the SERPs.
The trust score that the Knowledge Vault API provides to entities is a popular KPI. But it only tells part of the story, as it is heavily affected by:
News cycles. (More news, the score goes up and then down as the news cycle dies down.) Google’s understanding of the multifacetedness of the entity. (For example, as you understand more about a person’s multiple careers, the score is likely to drop.) Relationships with other entities. (An entity’s score will distort the scores of its nearest neighbors.)
Also, Google is removing this rating. Like PageRank, it will continue to exist, but we will no longer have access to the information.
As such, success can be measured by:
Keeping a stable KGID in the Knowledge Vault over time. Do not activate entity duplicates (this divides and dilutes NEEATT’s credibility equity). Building relationships with a large number of relevant related entities. Have an information-rich knowledge panel. Have an accurate knowledge panel.
You’re not alone (but you want to be)
This update sheds light on entity duplication, which is a particularly thorny issue for Person entities. This is due to Google’s approach to the ambiguity of people’s names.
Almost all of us share our names with other people. I share mine with at least 300 other Jason Barnards. I hate to think how many John Smiths and Marie Duponts there are.
When Google’s algorithms find and analyze a reference to a Person, they assume that person is someone they’ve never met before, unless multiple corroborating facts match and convince them otherwise.
This means that a duplicate can be created if there is a factually inaccurate reference to a Person entity or the reference does not have enough traits in common with an existing Person entity.
If this happens, any NEEATT credibility value referencing the duplicate is lost. This is the modern equivalent of link building, but linking to the wrong site.
When will the next update be?
Based on our historical data, over the past nine years, the pattern of entity updates is clear: December, February (or March) and July have consistently been the critical months.
In each of the last five years, July has seen the most impactful updates.
get ready Our experience building and optimizing thousands of entities is that you need to have all your corroboration straight 6-8 weeks before major updates. The next updates may be in July and December.
Google’s growing emphasis on person entities in its Knowledge Graph
Looking at the data from the July 2023 and March 2024 Killer Whale updates, I’m finally seeing the first signs that Google is starting to talk about “things, not strings” at scale.
The foundation of modern SEO is educating Google about your entities: the website owner, the content creators, the company, the founder, the CEO, the products, etc.
Without building a meaningful understanding in Google’s “brain” about who you are, what you offer, and why you are the most credible solution, you will no longer be in the “Google game.”
In a world of things, not strings, only if you can successfully feed Google’s knowledge graphs with facts will Google have the basic tools it needs to reliably figure out what problems you’re best in the market to solve for the subset of its users who are your audience.
Knowledge is power. In modern SEO, the ability to feed knowledge algorithms is the path to success.
The views expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
[ad_2]
Source link




